View distributions of isotypes and cell types, as well as GLT expression in specified subsets of cells, isotypes, and RA conditions.
Explore Isotype DataOur analysis of BCR isotypes makes use of the Human Immune Health Atlas B cell population definitions.
Explore B cell populationsBackground
Investigation and text authored by Marla Glass.
Data analysis by Lauren Okada.
Visualization tools by Zachary Thomson and Lucas Graybuck.
Class-switch recombination (CSR) is a key process in B cell maturation that alters the immunoglobulin heavy chain (IgH) constant region, affecting antibody function, lifespan, and interactions with effector molecules. CSR is crucial for humoral immunity, influencing both pathogen defense and autoimmune disease pathogenesis.
Sterile germline transcripts (GLT) from IgH constant genes are non-productive but serve as molecular markers for CSR (Matthews et al. 2014; Stavnezer 1996; Lorenz, Jung, and Radbruch 1995). Their presence signifies predisposition to CSR events (Xu et al. 2012; Roco et al. 2019) and can be detected in single-cell RNA sequencing (scRNA-seq) data if constant gene regions within transcripts are sufficiently preserved during library preparation and sequencing.
Rheumatoid Arthritis B Cell Isotype Explorer
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease marked by joint inflammation and bone destruction, often preceded by elevated anti-citrullinated protein antibodies (ACPA). To investigate B cell changes contributing to RA risk, we conducted a longitudinal study of ACPA+ at-risk individuals (ARI), one-third of whom developed RA. We identified a CD27- ITGAX+ ‘atypical’ B cell subset enriched for class-switched cells that increased in abundance during RA progression. Additionally, naive B cells in ARI showed heightened BCR signaling and were primed for IgG3 class-switching based on GLT expression analysis. These findings suggest ongoing B cell activation is a feature of RA progression.
Using an IgH constant gene order-based approach with 10x Genomics Chromium 3’ scRNA-seq data, we labeled productive BCR isotypes and identified non-productive GLT. This data exploration app allows you to browse BCR isotype-labeled B cell scRNA-seq data from ACPA+ at-risk individuals, those who progressed to RA, early RA patients, and ACPA- healthy controls.
Additional details on BCR isotype analysis and sterile germline expression methods are provided below.
Assumptions
- Non-switched B cells can express IGHD and IGHM simultaneously during certain developmental stages
- Switched B cells can only be expressing one productive BCR heavy chain or IgH isotype at a time
- If multiple genes are expressed, we are detecting sterile germline transcription
- In cases of concurrent multi-isotype expression, the gene nearest the 5’ end of the gene locus is the likely true isotype given the biological mechanisms of class-switch recombination
Other considerations
This isotype labeling and GLT analysis method cannot be applied to 10x Genomics Chromium 5’ gene expression data with the same accuracy, due to the orientation of the captured mRNA molecule having increased loss of IgH constant gene segments in cDNA fragmentation steps of library preparation.
Created with BioRender.com
Methods for B cell IgH Isotype Analysis
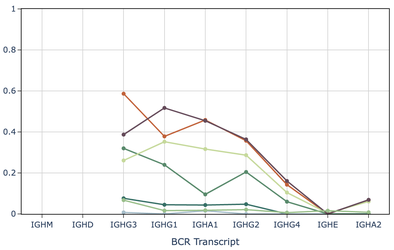
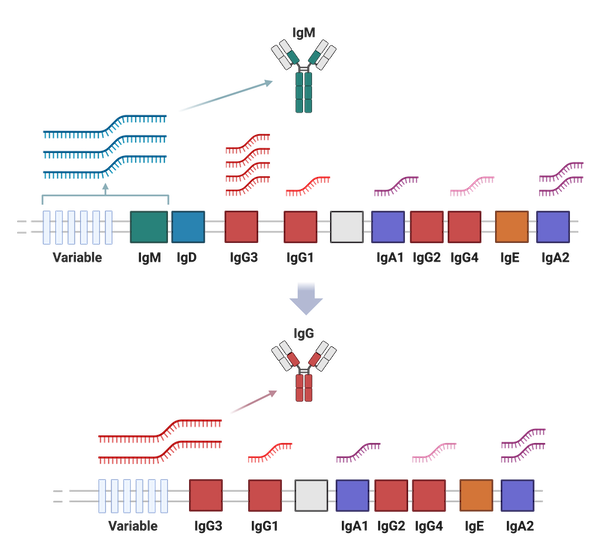
QC-processed 10x Genomics Chromium 3’ scRNA-seq data was used to estimate proportions of switched IgH isotype B cells in study samples. First, positive expression for each of the nine IgH constant genes (IGHM, IGHD, IGHG1-4, IGHA1-2, and IGHE) was defined per B cell as a normalized UMI count greater than or equal to 0.5 (normalized to 10,000 UMI per cell). Cells positive for either or both IGHM and IGHD were classified as ‘non-switched’ with isotype assignments of IGHM, IGHD, or IGHMD. The remaining cells were classified as ‘class-switched’ if positive for any other IGH gene. In cases of multi-positivity for class-switched genes, the positive gene located nearest the variable region in the genomic DNA was assigned as the isotype to be consistent with class-switch recombination biology (IgH constant region ‘switched’ loci order after the variable region: IGHG3, IGHG1, IGHA1, IGHG2, IGHG4, IGHE, IGHA2). Both the class-switched status and isotype for cells without detected IgH gene expression were denoted as ‘undetermined’. After isotype classification, IgH constant gene germline transcription (GLT) level was defined as the normalized gene counts for those IgH loci downstream of the isotype-determining gene. As an example, IgG3+ isotype B cells may have quantifiable GLT from the IGHG1, IGHA1, IGHG2, IGHG4, IGHE, and IGHA2 genes.
References
He Z, Glass MC, Venkatesan P, Feser ML, Lazaro L, Okada LY, et al. Systemic inflammation and lymphocyte activation precede rheumatoid arthritis. bioRxiv. 2024. p. 2024.10.25.620344.
doi:10.1101/2024.10.25.620344
Lorenz M, Jung S, Radbruch A. Switch transcripts in immunoglobulin class switching. Science. 1995;267: 1825–1828.
doi:10.1126/science.7892607
Matthews AJ, Zheng S, DiMenna LJ, Chaudhuri J. Regulation of immunoglobulin class-switch recombination: choreography of noncoding transcription, targeted DNA deamination, and long-range DNA repair. Adv Immunol. 2014;122: 1–57.
doi:10.1016/B978-0-12-800267-4.00001-8
Roco JA, Mesin L, Binder SC, Nefzger C, Gonzalez-Figueroa P, Canete PF, et al. Class-switch recombination occurs infrequently in germinal centers. Immunity. 2019;51: 337-350.e7.
doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2019.07.001
Stavnezer J. Immunoglobulin class switching. Curr Opin Immunol. 1996;8: 199–205.
doi:10.1016/s0952-7915(96)80058-6
Xu Z, Zan H, Pone EJ, Mai T, Casali P. Immunoglobulin class-switch DNA recombination: induction, targeting and beyond. Nat Rev Immunol. 2012;12: 517–531.
doi:10.1038/nri3216